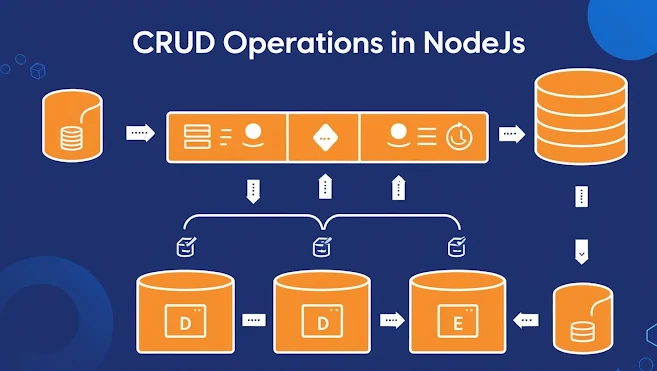
Step 1: Set Up Your NodeJs Project
Create a new project folder and initialize a NodeJs project:
mkdir node-crud-app
cd node-crud-app
npm init -y
Install required dependencies:
npm install express mongoose body-parser cors dotenv
Step 2: Create the Basic Server
Create a new file server.js and add the following code:
const express = require('express');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const cors = require('cors');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
require('dotenv').config();
const app = express();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 5000;
app.use(cors());
app.use(bodyParser.json());
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
.then(() => console.log('MongoDB Connected'))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send('Welcome to the CRUD API'); });
app.listen(PORT, () => { console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`); });
Step 3: Define a Mongoose Model
Create a folder models and inside it, create Item.js:
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const ItemSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: { type: String, required: true },
description: String,
createdAt: { type: Date, default: Date.now }
});
module.exports = mongoose.model('Item', ItemSchema);
Step 4: Implement CRUD Routes
Create a folder routes and inside it, create items.js:
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
const Item = require('../models/Item');
// CREATE an item
router.post('/', async (req, res) => {
try { const newItem = new Item(req.body); await newItem.save(); res.status(201).json(newItem); }
catch (err) { res.status(400).json({ message: err.message }); }
});
// READ all items
router.get('/', async (req, res) => {
try { const items = await Item.find(); res.json(items); }
catch (err) { res.status(500).json({ message: err.message }); }
});
// UPDATE an item
router.put('/:id', async (req, res) => {
try { const updatedItem = await Item.findByIdAndUpdate(req.params.id, req.body, { new: true }); res.json(updatedItem); }
catch (err) { res.status(400).json({ message: err.message }); }
});
// DELETE an item
router.delete('/:id', async (req, res) => {
try { await Item.findByIdAndDelete(req.params.id); res.json({ message: 'Item deleted' }); }
catch (err) { res.status(500).json({ message: err.message }); }
});
module.exports = router;
Step 5: Connect Routes to Server
Modify server.js to include the new routes:
const itemRoutes = require('./routes/items');
app.use('/items', itemRoutes);
Step 6: Test the API
Start your server:
node server.js
Test CRUD operations using Postman or cURL:
Create an item (POST):
POST http://localhost:5000/items
Body (JSON): { "name": "Laptop", "description": "A powerful laptop" }
Get all items (GET):
GET http://localhost:5000/items
Update an item (PUT):
PUT http://localhost:5000/items/{item_id}
Body (JSON): { "name": "Updated Laptop" }
Delete an item (DELETE):
DELETE http://localhost:5000/items/{item_id}
Conclusion
You now have a fully functional CRUD API using NodeJs, ExpressJs, and MongoDB!